M.Thermocouple Simulators for Calibration and Checkout of Electronic Equipment 用于电子设备校准和检查的热电偶模拟器
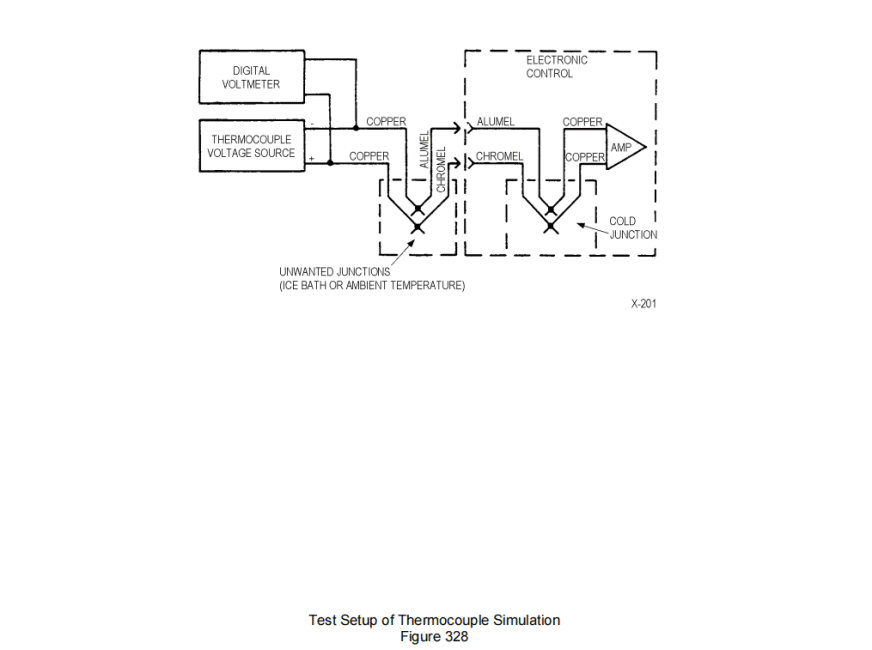
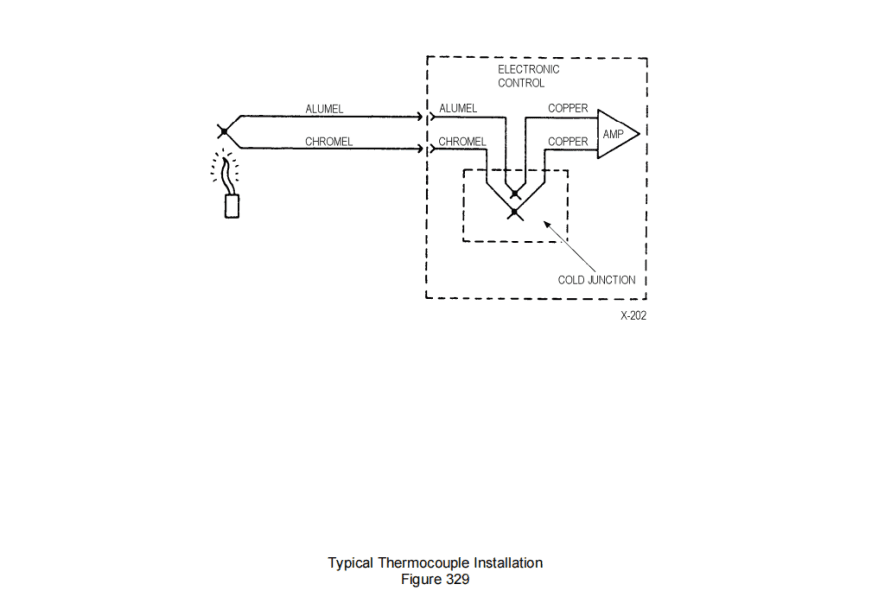
(1) For test purposes in simulating a thermocouple, a common and recommended method is shown in Figure 328 and Figure 330. Note that the voltmeter must be connected to the copper leads of the voltage source and not to the alumel and chromel input wires to the electronic control. The thermocouple junctions created by the thermocouple voltage source connections to the alumel-chromel wire are compensated by means of the ice bath. This is because the alumel-chromel thermocouple tables are based on an unwanted junction (reference junction or cold junction) at 32°F (0°C) the temperature of melting ice. The input leads to the electronic control are alumel and chromel wire, therefore, there are no thermocouple junctions, due to dissimilar metals, at the interface to the electronic control. A comparison of this thermocouple simulation to a typical thermocouple temperature measurement installation is shown in Figure 328.
在热电偶模拟测试中,常用且推荐的方法如图328和图330所示。需要注意的是,电压表必须连接到电压源的铜质引线,而非电子控制装置的氧化铝和铬铝输入导线。由热电偶电压源连接氧化铝-铬铝导线形成的热电偶接点,通过冰浴进行补偿。这是因为氧化铝-铬铝热电偶曲线基于冰晶融化温度(32华氏度/0摄氏度)处的非典型接点(参考接点或冷端)。由于电子控制装置的输入导线采用氧化铝和铬铝导线,因此在与电子控制装置的接触界面不存在因金属相异导致的热电偶接点。图328展示了该热电偶模拟系统与典型热电偶测温装置的对比示意图。
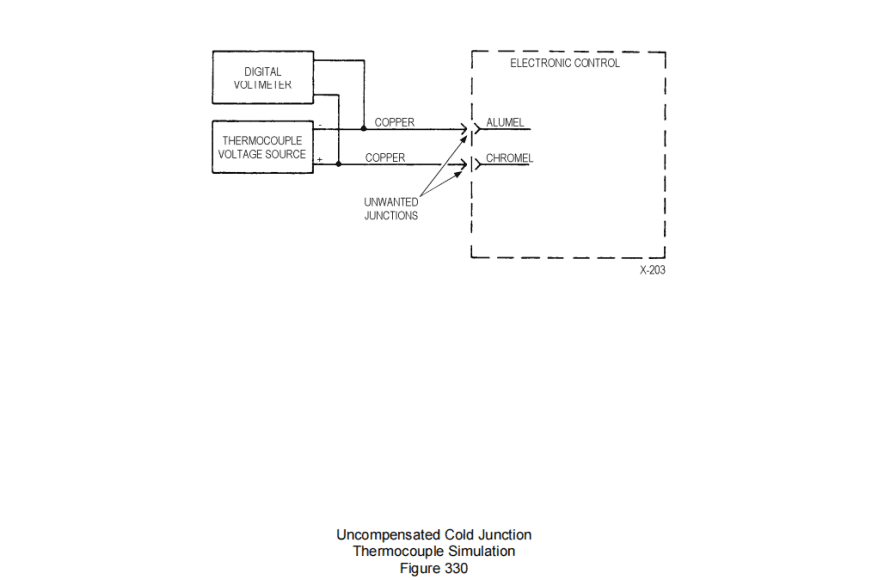
(2) Temperature simulation without using an ice bath or other compensation is used but must be well understood in order to avoid unwanted errors. The temperature of the unwanted junction, which is room temperature, must be measured accurately, and then used to correct the simulated input voltage.
不使用冰浴或其他补偿的温度模拟,但必须充分理解,以避免不必要的误差。必须精确测量不必要的结点(即室温)的温度,然后用于校正模拟输入电压。
(3) Using Figure 328 as an acceptable setup where the unwanted copper-alumel and chromel-copper junctions are at ambient temperature, then any voltage input from the thermocouple voltage source must be corrected for this existing ambient temperature input. Note that an ice bath was used for the junction temperature in the previous example.
使用图328作为可接受的设置,其中不需要的铜-铝和铬-铜结点处于环境温度下,然后必须根据现有的环境温度输入来校正热电偶电压源的任何电压输入。请注意,在之前的示例中,结点温度使用的是冰浴。
(4) For example, suppose the input required is 1200°F (648,8°C), and the room temperature is 77°F (25°C). To determine what voltage would be required from the thermocouple voltage source in Figure 328, refer to an alumel-chromel thermocouple table. The voltage for 77°F (25°C) is 1.000 millivolt, and 1200°F (648,8°C) is 26.975 millivolts. Since the circuit of this figure, with zero thermocouple source voltage, is inputting 1.000 millivolt (ambient of 77°F (25°C)), then the input required to simulate 1200°F (648,8°C) (26.975 millivolts) is:
例如,假设所需的输入为1200°F(648.8°C),室温为77°F(25°C)。要确定图328中热电偶电压源所需的电压,请参考铝铬热电偶表。77°F (25°C)时的电压为1.000毫伏,1200°F (648.8°C)时的电压为26.975毫伏。由于这个数字的电路,热电偶源电压为零,输入1.000毫伏(环境温度为77°F(25°C)),那么模拟1200°F(648.8°C)(26.975毫伏)所需的输入是:
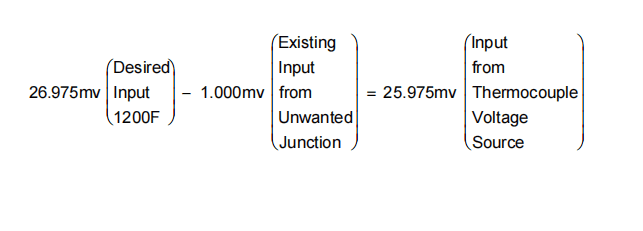
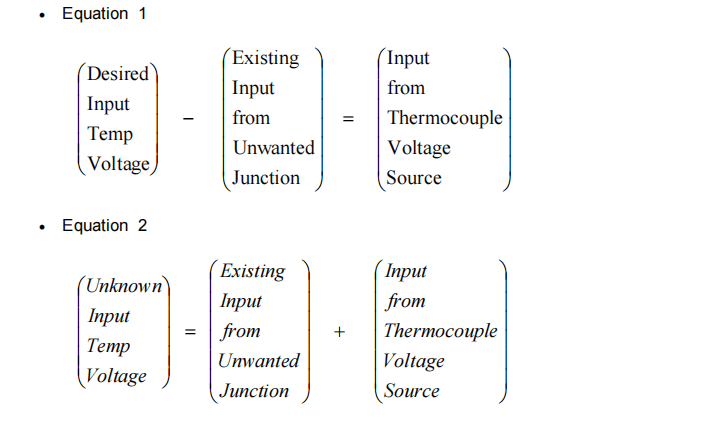
(5) In previous example the desired input voltage (temperature) was known and the unwanted junction voltage was subtracted from the desired input in order to obtain the correct voltage for the thermocouple voltage source. In the following example, Equation 2, the voltage of the thermocouple voltage source is known, such as when a temperature switch point is being checked, and the temperature associated with it is to be determined. In Equation 1 the desired input is Equation 2’s “unknown input”.
在前面的例子中,所需的输入电压(温度)是已知的,并且从所需的输入中减去不需要的结点电压,以获得热电偶电压源的正确电压。在下面的例子中,即公式2中,热电偶电压源的电压是已知的,例如当检查温度开关点时,需要确定与之相关的温度。在公式1中,所需的输入是公式2中的“未知输入”。
(6) Most electronic control temperature tolerances are on the order of ±20 to ±40°F. The temperature simulation circuit should be 10 times more accurate than the allowable tolerances for the electronic control. This means that the temperature simulation circuit should be accurate to within ±2 to ±4°F. This includes the errors in measurement of the room temperature for the cold junction voltage.
大多数电子控制温度公差在±20至±40°F之间。温度模拟电路的精确度应比电子控制的容许公差高10倍。这意味着温度模拟电路的精确度应在±2至±4°F之间。这包括冷端电压室温测量误差。
(7) Referring to an alumel-chromel thermocouple table, note that the millivolt reading for 1000F is 22.251 mv and for 1001F is 22.274 mv. The difference for this 1F Delta is 0.023 millivolts or 23 microvolts. This indicates that the voltmeter used for the thermocouple simulation voltage should have an accuracy and resolution of 0.01 millivolts or 10 microvolts. With such an accurate voltmeter, more error (1-1/2 to 3-1/2F) is allowed for the room temperature reading errors. Note that a 4F error in measuring the room temperature means a 4F error in calibrating the control.
参考铝铬热电偶表,注意1000F的毫伏读数为22.251 mv,1001F的毫伏读数为22.274 mv。1F的差值为0.023毫伏或23微伏。这表明用于热电偶模拟电压的电压表应具有0.01毫伏或10微伏的精度和分辨率。使用如此精确的电压表,室温读数误差允许更大的误差(1-1/2至3-1/2F)。请注意,测量室温时出现4F误差意味着校准控制时出现4F误差。






暂无评论内容